By Er Gurpreet Singh,
Senior Software Engineer,
Sopra Steria India
Showing posts with label Learn Java. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Learn Java. Show all posts
Thursday, 11 October 2018
Sunday, 19 November 2017
Saturday, 18 November 2017
Monday, 7 November 2016
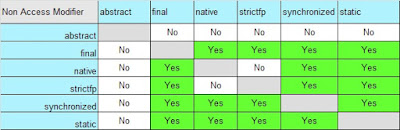
Which Non Access Modifier can be used which Non Access Modifier?
In Nutshell:
- abstract cannot be used with any other Non Access Modifier
- final can be used with all other Non Access Modifier except abstract
- synchronized can be used with all other Non Access Modifier except abstract
- native can be used with all other Non Access Modifier except abstract, strictfp
- strictfp can be used with all other Non Access Modifier except abstract, native
- static can be with all other Non Access Modifier except abstract
Thursday, 17 September 2015
How to use Comparator in java?
import java.util.*;
class ComparatorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Employee("B", 3));
list.add(new Employee("A", 1));
list.add(new Employee("C", 2));
Collections.sort(list, new EmployeeComparator());
for (Employee emp : list) {
System.out.println(emp.name + "\t" + emp.age);
}
}
}
class EmployeeComparator implements Comparator<Employee> {
@Override
public int compare(Employee o1, Employee o2) {
if (o1.age > o2.age) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
class Employee {
String name;
int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
Output:
B 3 C 2 A 1
Tuesday, 4 August 2015
Applet Demo 1
Source Code:
import java.applet.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo1 extends Applet
{
public void init()
{
//Code to run automatically
this.setSize(500, 500);
this.setBackground(Color.CYAN);
}
public void paint(Graphics g)
{
//now draw graphics
g.drawLine(0, 0, 100, 100);
g.drawRect(0, 0, 100, 100);
//change color of graphics
g.setColor(Color.blue);
g.drawString("Applet Demo", 0, 120);
}
}
Monday, 3 August 2015
Getting Started with Java GUI Programming
Download the Netbeans IDE from filehippo.com/download_netbeans
Also download Java JDK(32-bit or 64-bit) according to your operating system. For 32-bit operating system download the 32-bit version of Java JDK and for 64-bit operating system download the 64-bit version of Java JDK
After downloading firstly install Java JDK and then Netbeans
Sunday, 2 August 2015
for each loop in java
What is for each loop?
for each loop in java is the enhanced version of for loop. It is introduced from JDK 5. It is used to iterate all elements of an array or Collection.
Syntax:
for ( data-type variableName : array or collection )
{
//statements
}
Consider the following program:
for each loop in java is the enhanced version of for loop. It is introduced from JDK 5. It is used to iterate all elements of an array or Collection.
Syntax:
for ( data-type variableName : array or collection )
{
//statements
}
Consider the following program:
public class ForEachLoop
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] array ={ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
System.out.println("Array elements: ");
for(int element: array)
System.out.print(element+" ");
}
}
Write the above program in Notepad and save it as ForEachLoop.java
Compile and run it to get the following output:
Array elements:
1 2 3 4 5
the loop for(int element: array)
fetches the elements of array and assign it to variable element so we can use element to access the elements of array
Consider the following program to access elements of multi-dimensional array
Compile and run it to get the following output:
Array elements:
1 2 3 4 5
the loop for(int element: array)
fetches the elements of array and assign it to variable element so we can use element to access the elements of array
Consider the following program to access elements of multi-dimensional array
public class ForEachLoop
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] array ={ {1, 2, 3, 4,},{ 5,6,7,8} }; //array with 2 rows and 4 columns
System.out.println("Array elements: ");
for(int[] row: array)
for(int element: row)
System.out.print(element+" ");
}
}
Write the above program in Notepad and save it as ForEachLoop.java
Compile and run it to get the following output:
Array elements:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
the loop for(int[ ] row: array)
fetches one row of array and assign it to variable row so we can use row to access one row(or one dimensional array) of array
the loop for(int element: row)
fetches the elements of row and assign it to variable element so we can use element to access the elements of row
Compile and run it to get the following output:
Array elements:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
the loop for(int[ ] row: array)
fetches one row of array and assign it to variable row so we can use row to access one row(or one dimensional array) of array
the loop for(int element: row)
fetches the elements of row and assign it to variable element so we can use element to access the elements of row
Command Line Arguments
public class CommandLineArguments
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Total number of Command Line Arguments: "+args.length);
System.out.println("Command Line Arguments:");
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++)
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
}
Type the above program in Notepad and Save it as CommandLineArguments.java
Compile like this:
javac CommandLineArguments.java
Run like this:
java CommandLineArguments Arguments
For example:
java CommandLineArguments Hello World
output:
Total number of Command Line Arguments: 2
Command Line Arguments:
Hello
World
If you run like this:
java CommandLineArguments
output:
Total number of Command Line Arguments: 0
Command Line Arguments:
Note: Each argument in command line arguments is seperated by a space
Compile like this:
javac CommandLineArguments.java
Run like this:
java CommandLineArguments Arguments
For example:
java CommandLineArguments Hello World
output:
Total number of Command Line Arguments: 2
Command Line Arguments:
Hello
World
If you run like this:
java CommandLineArguments
output:
Total number of Command Line Arguments: 0
Command Line Arguments:
Note: Each argument in command line arguments is seperated by a space
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)